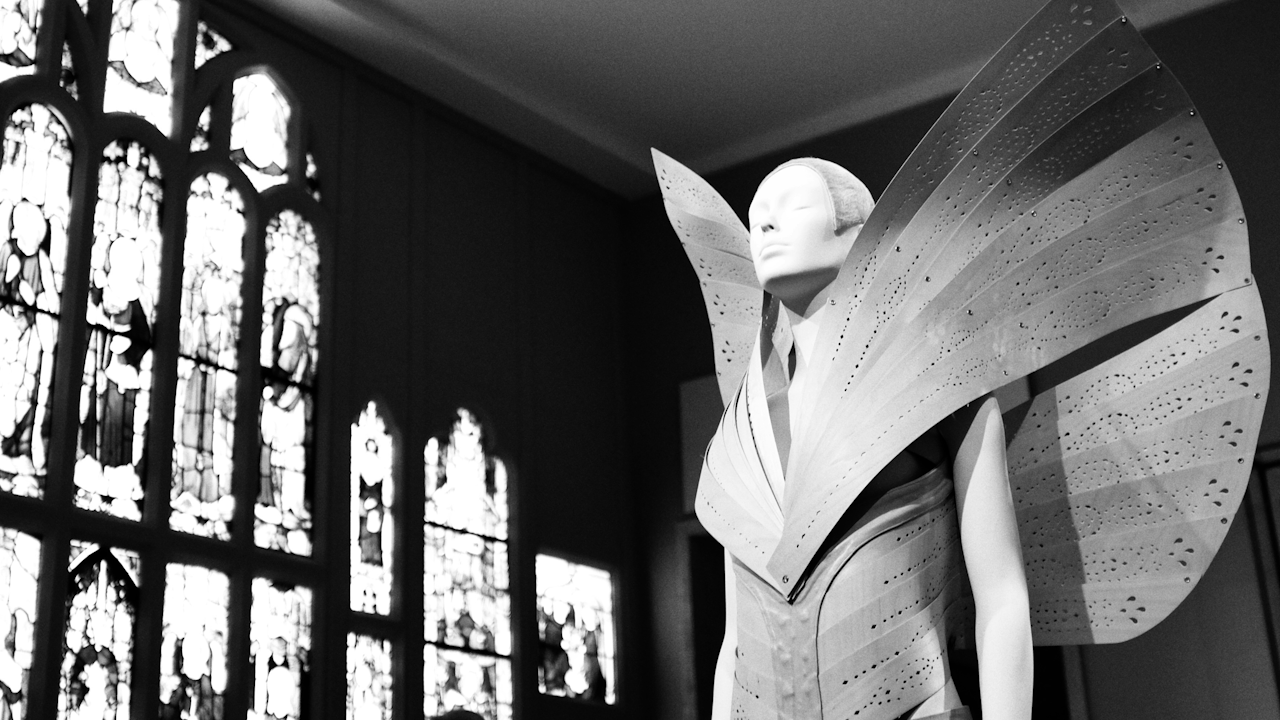
Introduction to 3D-Printed Fashion
The evolution of garment production has undergone a remarkable transformation with the advent of 3D printing technology. This innovative method, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs by layering materials. In the fashion industry, 3D-printed fashion represents a fusion of creativity and technology, offering designers unprecedented opportunities to push the boundaries of traditional garment creation.
Historically, the fashion industry has been characterized by a linear production process that often leads to waste and inefficiencies. However, with the integration of 3D printing, designers are now able to create complex structures and customize patterns with ease. This technology empowers them to conceptualize and bring to life intricate designs that would have been challenging or impossible to achieve through conventional means. Furthermore, 3D printing allows for on-demand production, significantly reducing overproduction and minimizing environmental impact.
Over the past decade, a growing number of fashion designers and brands have embraced 3D printing, recognizing its potential not only for mass customization but also as a means of artistic expression. From avant-garde runway pieces to wearable everyday items, 3D-printed fashion showcases the versatility of this technology. These innovations span various materials, including plastics, metals, and even textiles, enabling designers to explore unique aesthetics and functional attributes.
As the fashion landscape continues to evolve, the impact of 3D printing is becoming increasingly evident. Consumers are now drawn to bespoke pieces that reflect their individuality, while designers harness the potential of technology to bring their visions to life. In this ongoing dialogue between creativity and technical innovation, 3D-printed fashion stands out as a significant development, reshaping the industry’s future and opening doors to new processes and materials.
The Fusion of Art and Technology in Fashion Design
The intersection of art and technology in fashion design has been irrevocably transformed by the advent of 3D printing. This innovative technology allows fashion designers to explore new avenues for creativity, freeing them from the constraints of traditional manufacturing processes. With 3D printing, designers can experiment with complex patterns, customized fits, and intricate textures that would be challenging to achieve using conventional materials and techniques.
One of the most notable advantages of 3D printing in fashion is the ability to create unique silhouettes and structures that provide limitless design possibilities. For instance, designers can construct garments that feature intricate geometries, creating visually striking pieces that often serve as wearable art. This technology also facilitates the production of tailored clothing that dramatically improves fit and comfort, addressing the long-standing issue of standardized sizing that often leaves consumers unsatisfied.
Pioneering designers have already embraced 3D printing in their collections, illustrating the potential of blending artistic expression with cutting-edge technology. For example, the acclaimed designer Iris van Herpen is renowned for her innovative use of 3D printing techniques, integrating them seamlessly into her haute couture collections. Her designs often showcase elaborate textures and extraordinary craftsmanship, pushing the boundaries of what is possible within the realm of fashion. Another remarkable case is the collaboration between fashion designer Julia Koerner and the architectural firm, which resulted in stunning 3D-printed dresses inspired by natural forms. These examples underscore the profound impact that 3D printing has had on the creative landscape of fashion, enabling designers to manifest their visions in ways that were previously unimaginable.
In this evolving landscape, the fusion of art and technology continues to reshape the fashion design industry, encouraging creativity and innovation while enhancing the consumer experience. As more designers adopt 3D printing methods, the traditional definitions of fashion and art are destined to change, leading to a vibrant future that harmoniously marries the two realms.
Sustainability and Future Trends in 3D-Printed Fashion
The intersection of sustainability and technology within the fashion industry presents an intriguing paradigm shift, particularly through the lens of 3D-printed fashion. One of the most significant advantages of this innovation lies in its capacity to minimize waste. Traditional manufacturing processes often lead to surplus materials, whereas 3D printing utilizes additive manufacturing techniques. This approach allows brands to produce items layer by layer, thereby significantly reducing excess fabric and other materials that would typically contribute to landfills.
Moreover, the materials employed in 3D printing are frequently selected for their sustainability credentials. Many brands are exploring bioplastics, recycled materials, and biodegradable substances that align with environmentally conscious values. This progressive shift not only addresses the ecological impact of production methods but also encourages the use of ethical practices throughout the supply chain. As the technology evolves, it is expected that more innovative materials will emerge, enhancing the sustainability profile of 3D-printed fashion even further.
Looking to the future, the potential of 3D-printed fashion extends beyond waste reduction and sustainable materials. It is likely to influence consumer behavior significantly. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, there is a growing demand for transparency and ethics in production. Brands that adopt 3D printing technologies can better cater to this market by offering custom, made-to-order clothing that minimizes overproduction and aligns with individual consumer needs.
This trend toward personalized fashion can also drive a shift in fast fashion paradigms, as consumers may begin to favor quality and sustainability over quantity. Ultimately, the integration of 3D printing technology in fashion holds the promise of a more sustainable and ethical industry, paving the way for a future where eco-conscious practices are the norm rather than the exception.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing in Fashion
Despite the revolutionary potential of 3D printing in the fashion industry, several challenges and limitations must be addressed for its successful integration. One significant hurdle stems from technical constraints associated with the current state of 3D printing technology. Various materials, while innovative, may lack the versatility and durability required for everyday fashion. The fineness of details and the structural integrity of the printed garments are often inadequate when compared to traditional textiles. Consequently, designers may find it challenging to produce high-quality and fashionable items that meet consumers’ expectations.
Scalability is another pressing concern. While 3D printers can produce unique and customized pieces, the process remains slow compared to mass production methods. When catering to large-scale markets, brands may find it economically unviable to rely solely on 3D printing, thus limiting its widespread adoption. Additionally, the cost implications associated with 3D printing technologies, materials, and the necessary skilled labor can be prohibitive, especially for small designers or startups looking to enter the fashion industry.
Consumer acceptance also poses a challenge. While there is a growing segment of environmentally-conscious buyers interested in sustainable fashion, the general public may perceive 3D-printed items as less desirable or lacking the prestige associated with traditional couture. The perception of novelty can also deter consumers who prefer the established aesthetics and authenticity of conventional fashion products.
Looking forward, potential solutions may emerge in the form of innovative materials, advancements in printing technology, and improved techniques for combining 3D-printed elements with traditional textiles. By fostering collaboration between technologists and fashion designers, the industry can overcome these barriers, paving the way for 3D-printed fashion to coexist with established manufacturing practices.