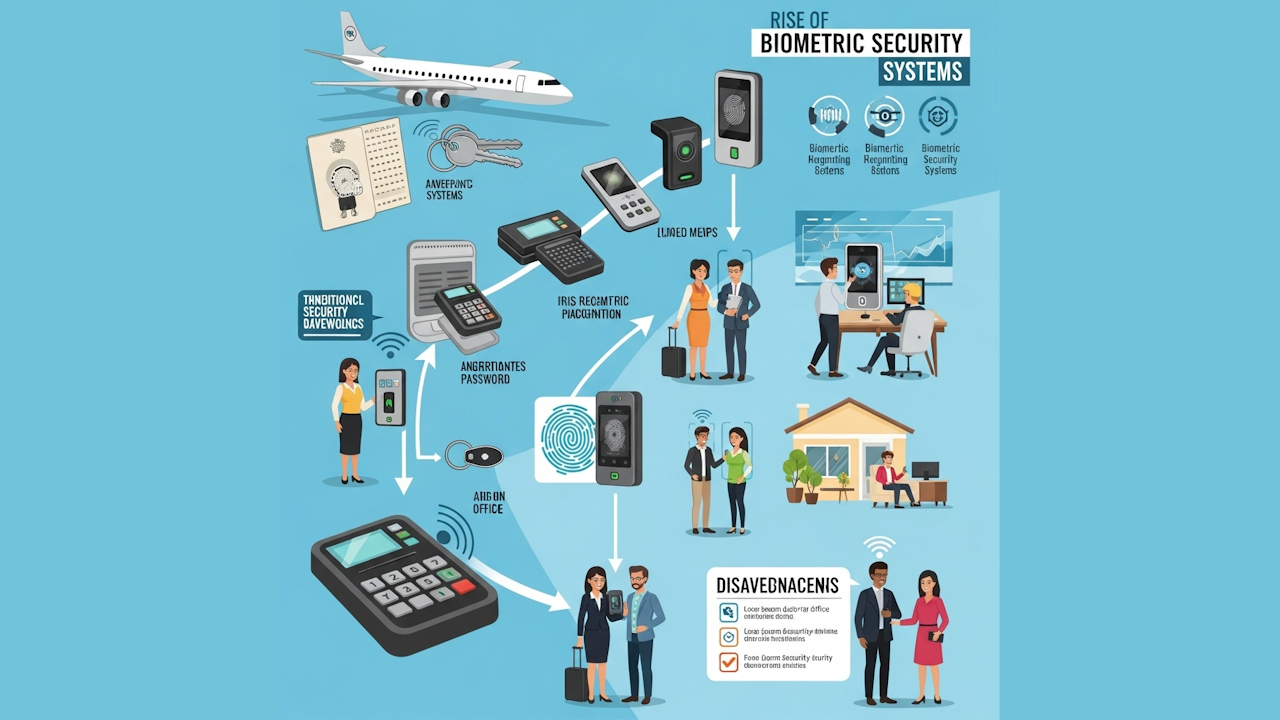
Biometric security systems have rapidly emerged as a dominant force in the landscape of modern security technologies. As traditional security methods such as passwords and PINs become increasingly vulnerable to breaches, biometric authentication provides a more secure and user-friendly alternative. This shift reflects the growing need for advanced protection in an age where digital threats are more sophisticated and pervasive than ever before.
Biometric security refers to the use of unique physical and behavioral characteristics for identity verification and access control. This technology leverages biological attributes such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, and voice recognition to authenticate users. Each of these identifiers is distinct to the individual, making biometric systems inherently difficult to forge or bypass. As a result, biometrics are becoming an integral part of security protocols across various industries.
The development and adoption of biometric security systems have been propelled by advances in technology and the increasing frequency of cyberattacks. Traditional password-based systems are prone to hacking, phishing, and human error, leaving sensitive information exposed. Biometric authentication addresses these vulnerabilities by providing a more personalized and robust security measure. The widespread availability of high-resolution cameras, advanced sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI) has further facilitated the integration of biometrics into everyday devices and applications.
One of the primary drivers behind the rise of biometric security systems is the proliferation of smartphones and other smart devices. Most modern smartphones are equipped with fingerprint scanners and facial recognition technology, allowing users to unlock their devices and authenticate transactions effortlessly. This seamless integration has increased public familiarity and comfort with biometric systems, encouraging broader adoption across multiple sectors. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies increasingly rely on biometric authentication to safeguard sensitive information and enhance user verification processes.
The financial sector has been particularly eager to embrace biometric security systems. With the increasing prevalence of online banking and digital transactions, financial institutions face mounting pressure to protect customer data and prevent fraud. Biometric authentication offers a solution by providing an additional layer of security that is difficult to replicate or exploit. For example, many banking apps now feature fingerprint and facial recognition options for secure access. This advancement not only enhances security but also improves user experience by eliminating the need for complex passwords and multi-factor authentication.
Healthcare is another industry where biometric security systems are playing a transformative role. Patient records contain highly sensitive personal information, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Implementing biometric authentication in healthcare settings helps ensure that only authorized personnel can access patient data. Furthermore, biometric systems can facilitate patient identification, reducing the risk of medical errors and improving the accuracy of healthcare delivery. Biometric technologies such as palm vein recognition and iris scanning are increasingly being deployed to safeguard medical records and streamline patient verification processes.
Government agencies worldwide are also investing heavily in biometric security systems to strengthen national security and improve public services. Biometric passports, national ID programs, and border control initiatives rely on fingerprint and facial recognition to authenticate identities and prevent identity fraud. In many countries, biometric data collection is becoming a standard practice for visa applications and law enforcement databases. This implementation enhances the ability of governments to track and manage individuals while minimizing the risks associated with identity theft and document forgery.
The adoption of biometric security systems is not limited to large organizations and government bodies. The consumer market has also witnessed significant growth in biometric-enabled devices. Smart home systems, for instance, frequently incorporate facial recognition and fingerprint scanning to regulate access. Biometric locks provide a higher level of security than traditional key-based systems, offering homeowners greater control and peace of mind. Wearable devices, including fitness trackers and smartwatches, are also integrating biometric sensors to monitor health metrics while simultaneously offering secure access to digital environments.
Despite the numerous advantages of biometric security systems, their rise also raises important ethical and privacy concerns. The collection and storage of biometric data pose significant risks if not managed responsibly. Unlike passwords, biometric identifiers cannot be easily changed if compromised. This reality underscores the need for stringent data protection measures and transparent policies regarding the use and retention of biometric information. Furthermore, concerns about surveillance and the potential misuse of biometric data highlight the importance of establishing clear regulatory frameworks to protect individual privacy rights.
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence and machine learning has also influenced the evolution of biometric security systems. AI-driven biometric technologies are capable of analyzing and authenticating identities with remarkable accuracy and speed. Deep learning algorithms enable systems to adapt to subtle changes in appearance and behavior, enhancing their ability to identify individuals under diverse conditions. This dynamic capability is particularly valuable in high-security environments where rapid and precise identity verification is crucial.
Global events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, have further accelerated the adoption of biometric security systems. The need for contactless authentication solutions has become paramount to minimize physical interaction and reduce the risk of virus transmission. Facial recognition and iris scanning have gained traction as touchless alternatives to fingerprint-based systems. Airports, public transportation hubs, and healthcare facilities increasingly rely on these technologies to ensure both security and public health.
The future of biometric security systems is poised for continuous innovation and widespread adoption. Emerging trends include the development of multi-modal biometric systems that combine multiple biometric identifiers for enhanced accuracy and security. Additionally, advances in biometric cryptography aim to integrate biometric authentication with encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive data further. The rise of decentralized biometric systems, where users retain control over their biometric information, represents another promising direction for the industry.
As digital landscapes evolve and security threats become more sophisticated, the demand for biometric security systems is expected to grow exponentially. These technologies offer a compelling balance of security, convenience, and efficiency, making them a critical component of modern security strategies. With ongoing technological advancements and increased public acceptance, biometric security systems are set to play an even more prominent role in shaping the future of digital security and identity verification.