The Role of Hormones in Emotional Regulation
Hormones act as crucial chemical messengers in the human body, orchestrating a multitude of physiological processes including emotional regulation. The influence of these hormones on mood is profound, as they communicate with various tissues and organs, impacting both psychological and physical well-being. Among the key hormones involved in mood dynamics are serotonin, dopamine, cortisol, and oxytocin, each functioning in distinct yet interconnected manners to promote emotional stability.
Serotonin, often referred to as the ‘feel-good hormone’, plays a pivotal role in mood regulation. Higher levels of serotonin are generally associated with feelings of happiness and well-being, while lower levels can lead to mood disorders such as depression. This hormone’s intricate relationship with mood underscores the critical importance of balanced serotonin levels in maintaining mental health.
Dopamine, another central player in emotional health, is linked to the brain’s reward system. It influences feelings of pleasure and satisfaction, essential for motivation and reinforcement of positive behaviors. The dysregulation of dopamine can contribute to mood disorders and is often observed in conditions like depression and bipolar disorder.
Cortisol, frequently described as the ‘stress hormone,’ presents a contrasting role. While it is essential for the body’s stress response, excessive cortisol levels can negatively affect mood, leading to anxiety and depression. Understanding the fluctuations of cortisol is vital for appreciating its impact on emotional states, particularly during stressful life events.
Lastly, oxytocin, known for its involvement in social bonding and emotional connection, also plays a significant role in how individuals experience and express emotions. This hormone fosters feelings of trust and intimacy, impacting overall emotional health.
The interplay between these hormones and mood underscores the importance of hormonal balance in emotional well-being. Fluctuations in hormonal levels can significantly affect mood and contribute to various mood disorders, emphasizing the need for further investigation into hormonal health as an avenue for enhancing emotional stability.
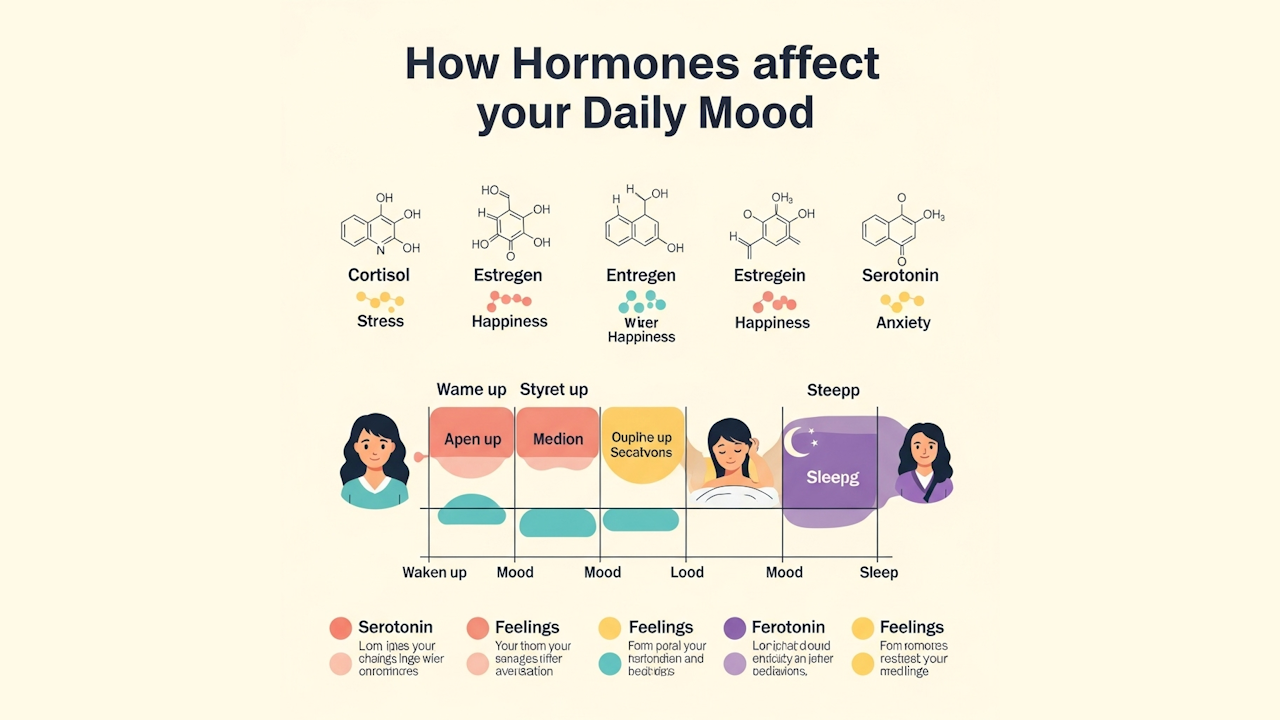
Hormonal Fluctuations Throughout the Day
Hormones play a vital role in regulating our daily moods, influenced largely by the natural circadian rhythms of the body. These rhythms dictate the patterns of hormone release, leading to fluctuations that can significantly impact emotional and mental states. For instance, cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, reaches its peak levels in the early morning. This surge in cortisol is crucial for promoting alertness and preparing the body for the day ahead. As daylight progresses, levels of cortisol gradually decline, allowing for a more balanced mood as the day unfolds.
In contrast, as evening approaches, the body transitions into a state of rest and recuperation. Here, melatonin—the hormone associated with sleep—begins to rise steadily. This increase in melatonin is essential for signaling to the body that it is time to wind down, facilitating better sleep quality and thereby supporting emotional stability. The interplay between cortisol and melatonin illustrates the importance of hormonal timings in our daily life and its correlation with mood variations.
To effectively manage these hormonal fluctuations, lifestyle changes can be immensely beneficial. Incorporating regular physical activity, for instance, helps to regulate cortisol levels, minimizing potential spikes that could lead to heightened anxiety or stress. A balanced diet enriched with nutrients that support hormonal health, such as omega-3 fatty acids, also plays a critical role in mood stabilization. Furthermore, adhering to proper sleep hygiene—maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, reducing blue light exposure in the evening, and creating a calming bedtime routine—can enhance melatonin production, ensuring a restorative night’s sleep.
Recognizing and understanding these hormonal patterns is not merely academic; rather, it forms the foundation for adopting healthier habits that can lead to improved mood throughout the day. By proactively managing these dynamics, individuals can support emotional well-being and enhance their overall quality of life.
Hormonal Influences by Life Stages and Events
Hormones play a pivotal role in governing our emotional responses throughout various life stages. During puberty, the onset of hormonal changes can lead to pronounced mood swings. As adolescents experience fluctuations in hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, they may become more sensitive or irritable. This period is marked by rapid physical and emotional development, which can complicate social interactions and self-esteem, leading to a heightened sense of anxiety and mood variability.
Moving into adulthood, the menstrual cycle introduces another layer of hormonal influence on mood. Many women report experiencing mood changes during the premenstrual phase, often linked to varying levels of estrogen and progesterone. Symptoms may include irritability, sadness, or increased sensitivity. Understanding these patterns is crucial; recognizing that these fluctuations are temporary can help mitigate emotional responses and improve coping strategies. Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and practicing mindfulness techniques can be effective in managing these symptoms.
Pregnancy also signifies a period of dramatic hormonal transitions. The surge in hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone can affect mood, leading to episodes of anxiety or depression. Postpartum hormones can further exacerbate these feelings, underscoring the importance of support systems and professional help during this time. Women experiencing postpartum mood disorders should consider seeking professional guidance to effectively navigate these challenges.
Meanwhile, menopause brings a significant shift as estrogen levels decline, resulting in emotional instability for many women. Common symptoms include increased irritability, sadness, and anxiety. Understanding that these shifts are a natural physiological process can be empowering. Integrating healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress-reducing practices, can greatly assist in managing these hormonal changes and their emotional repercussions.
Lastly, it is crucial to recognize external stressors’ influence on hormonal levels. Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol production, which may exacerbate feelings of anxiety and irritability. Identifying stressors and developing coping mechanisms, such as relaxation techniques and support networks, can aid in maintaining emotional equilibrium during challenging times.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Effect on Hormonal Health
The intricate relationship between lifestyle choices and hormonal health plays a significant role in influencing our mood and overall well-being. Nutrition, physical activity, and stress management are crucial aspects to consider when addressing hormonal balance. A well-rounded diet rich in mood-boosting foods can enhance hormonal function and, consequently, improve mood stability. Foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are known to support hormone production and reduce inflammation. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into one’s diet helps ensure that the body receives essential nutrients that facilitate optimal hormonal health.
Regular physical activity is another vital component that affects hormonal levels. Engaging in consistent exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also promotes the release of endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” hormones. Exercise has been associated with increased levels of serotonin and dopamine, which play significant roles in mood regulation. Whether through aerobics, strength training, or even leisurely walks, adhering to an exercise routine fosters hormonal balance and contributes to emotional well-being.
Moreover, stress management is critical when addressing hormonal health. Chronic stress can trigger the overproduction of cortisol, the stress hormone, which can lead to mood swings and other emotional disturbances. Mindfulness practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help individuals cope with stress more effectively. These activities encourage relaxation and can significantly mitigate the negative impact of stress on hormone levels.
For individuals experiencing persistent mood issues tied to hormonal imbalances, seeking professional guidance is advisable. Healthcare providers can offer tailored strategies to address specific concerns, including lifestyle adjustments and appropriate interventions. By understanding and modifying their lifestyle choices, readers can take proactive steps toward nurturing their hormonal health and enhancing their mood on a daily basis.